Malthusian Theory of Population
The Malthusian Theory of Population is the theory of exponential growth of population and arithmetic growth of food supply. The theory was proposed by Thomas Robert Malthus. He believed that a balance between population growth and food supply can be established through preventive and positive checks.
Major Elements of the Malthusian Theory
1. Population and Food Supply : The Malthusian theory explained that the population grows in a geometrical fashion. The population would double in 25 years at this rate. However, the food supply grows in an arithmetic progression. Food supply increases at a slower rate than the population. That is, the food supply will be limited in a few years. The shortage of food supply indicates an increasing population.
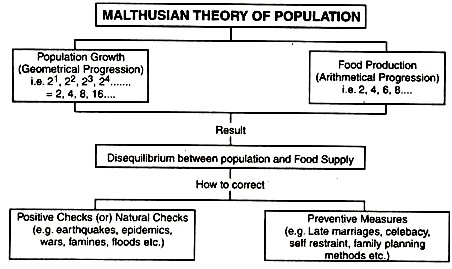
2. Checks on Population : When the increasing population rate is greater than the food supply, disequilibrium exists. As a result, people will not get enough food even for survival. People will die due to a lack of food supply. Adversities such as epidemics, wars, starvation, famines and other natural calamities will crop up which are named as positive checks by Malthus. On the contrary, there are man-made checks known as preventive checks.
3. Positive Checks : Nature has its own ways of keeping a check on the increasing population. It brings the population level to the level of the available food supply. According to Malthus nature plays when the population growth goes out of control.
4. Preventive Checks : Preventive measures such as late marriage, self-control and simple living, help to balance the population growth and food supply. These measures not only check the population growth but can also prevent the catastrophic effects of the positive checks.
Criticism of Malthusian Theory of Population
The Malthusian theory was criticized based on the following observations:
- In Western Europe, the population was rising at a rapid rate. At the same time, the food supply had also increased due to technological developments.
- On many occasions, food production had increased more than the population. For eg., 2% of the total population is working in the agricultural sector in the US. Still, the total GDP is more than 14 trillion dollars.
- Malthus’s theory stated that one of the reasons for limited food supply is the non-availability of land. However, the amount of food supply in various countries has increased due to increased globalization.
- The estimations for the geometric growth of population and arithmetic growth of population were not provided by Malthus. It was stated that the rate of growth is not consistent with Malthus’ theory.